Oral Health
Cavities in Teeth: Causes, Prevention, and Effective Treatments
July 23, 20242 Mins read855 Views
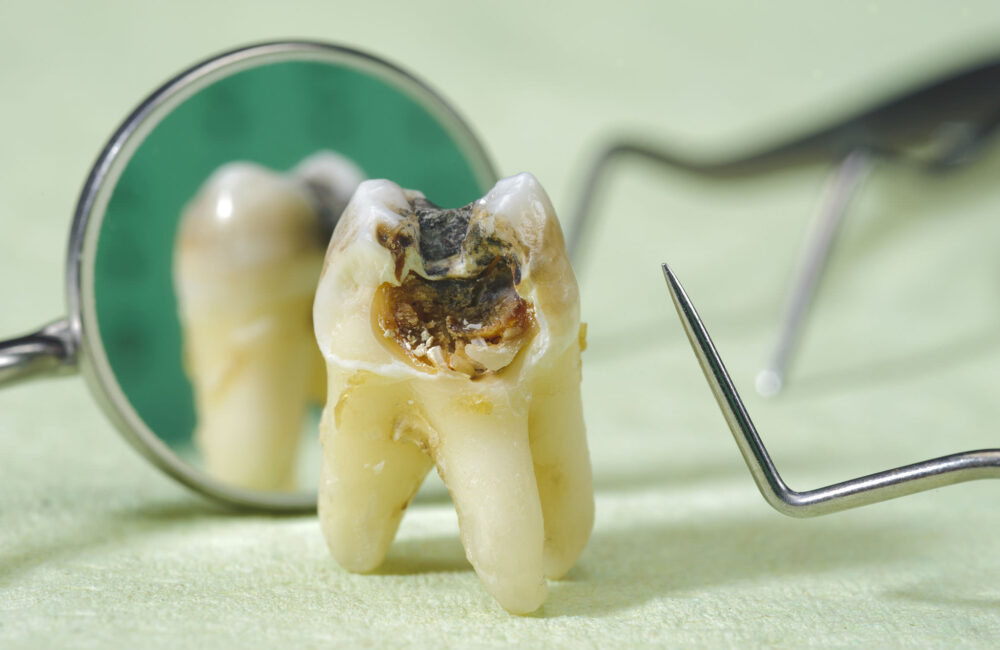
tooth with dental caries
Cavities, also known as dental caries, are a common dental issue affecting people of all ages. They occur when Cavities, also known as dental caries, are a common dental issue affecting people of all ages. They occur when the hard surface of your teeth is damaged, leading to tiny holes. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding cavities, their causes, prevention, and treatment.
What Causes Cavities?
- Plaque Buildup: Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. When you consume sugary or starchy foods, the bacteria in plaque produce acids that attack tooth enamel.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque accumulation, increasing the risk of cavities.
- Dietary Choices: Frequent snacking and consuming sugary drinks contribute to the development of cavities.
- Dry Mouth: Saliva helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids. Thus, a lack of saliva can increase cavity risk.
How to Prevent Cavities
- Brush Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque. Additionally, consider using an electric toothbrush for a more thorough clean.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps clean the spaces between your teeth where a toothbrush can’t reach. As a result, it prevents plaque buildup in those areas.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce your intake of sugary snacks and drinks. Instead, opt for healthier options like fruits and vegetables.
- Use Mouthwash: An antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in your mouth, thereby lowering the risk of cavities.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. Consequently, this helps catch cavities early and prevents more serious dental issues.
Treatment Options for Cavities
- Fluoride Treatments: In the early stages, fluoride treatments can help restore enamel and sometimes reverse a cavity.
- Fillings: If a cavity has formed, your dentist will remove the decayed part and fill the space with a material like resin, gold, or silver amalgam.
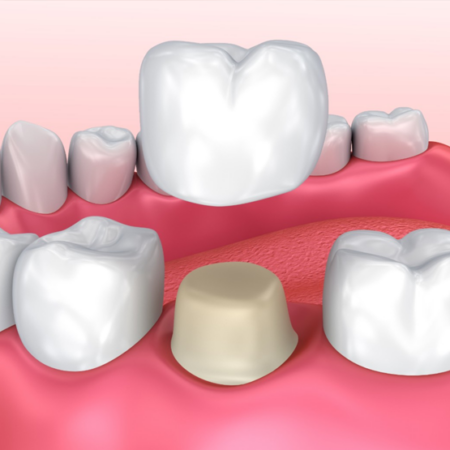
- Crowns: For extensive decay, a crown may be needed to cover and protect a tooth. Therefore, this option is often used when a filling is insufficient.
- Root Canals: If decay reaches the inner material of your tooth (pulp), a root canal may be necessary. This procedure removes the infected pulp and seals the tooth.
- Tooth Extractions: In severe cases, if a tooth cannot be saved, it may need to be removed. Consequently, you might consider a dental implant to replace it.
Conclusion
In summary, cavities are a preventable and treatable dental condition. By maintaining good oral hygiene and making smart dietary choices, you can significantly reduce your risk. Remember, regular dental visits are crucial for catching cavities early and keeping your smile healthy.
Stay tuned for more actionable oralhealth tips and advice by visiting udenz.io
0
Shares