Understanding Bone Grafts in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Guide
Bone grafts play a crucial role in modern dental practices, significantly contributing to restorative and reconstructive dental procedures. This blog provides an in-depth look at what bone grafts are, why dentists use them, and what patients can expect during and after the procedure.
What is a Bone Graft?
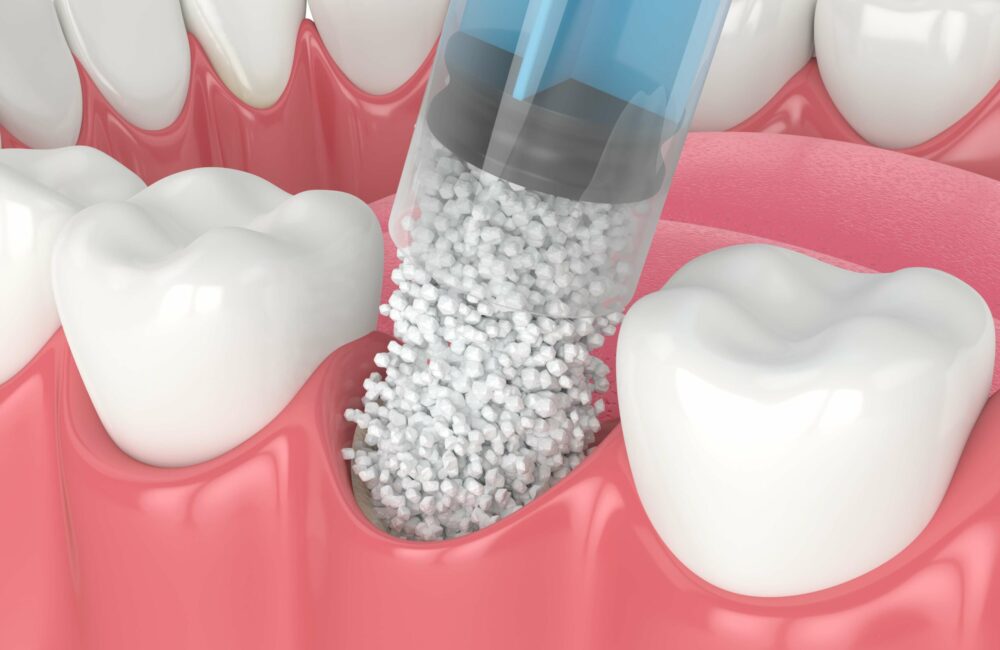
In dentistry, a bone graft involves transplanting bone tissue to augment or replace missing bone in the jaw. This procedure becomes essential for patients who have experienced bone loss due to periodontal disease, tooth loss, or trauma. The graft restores the bone structure and creates a stable foundation for dental implants or other restorative procedures.
Types of Bone Grafts
Dentists use several types of bone grafts, each with specific applications and benefits:
- Autografts: These grafts come from the patient’s own body, typically from the hip or another part of the jaw. Because they are biocompatible and have a high success rate, dentists consider autografts the gold standard.
- Allografts: These grafts are sourced from a donor, usually from a bone bank. The processing ensures safety and reduces the risk of rejection or infection.
- Xenografts: These grafts are derived from animals, commonly bovine (cow) sources. The processing makes xenografts safe for human use and effectively supports bone growth.
- Alloplasts: These synthetic bone grafts are made from biocompatible materials such as calcium phosphate. Alloplasts offer an excellent option for patients who prefer not to use human or animal bone.
Why are Bone Grafts Necessary?
Bone grafts serve several essential purposes:
- Dental Implants: Patients considering dental implants need sufficient bone density to anchor the implant securely. Bone grafts rebuild the jawbone to provide a stable foundation.
- Bone Loss Prevention: Following tooth extraction or loss, the jawbone can begin to deteriorate. Bone grafts preserve bone structure and prevent further bone loss.
- Restoring Facial Structure: Significant bone loss can affect the shape and structure of the face. Bone grafts restore a more natural appearance by rebuilding the jawbone.
The Bone Graft Procedure
The bone graft procedure typically involves several steps:
- Consultation and Planning: Your dentist or oral surgeon will evaluate your dental health, review your medical history, and determine the type of bone graft needed.
- Anesthesia: The dental team will administer local or general anesthesia to ensure your comfort during the procedure.
- Graft Placement: The dentist makes an incision in the gum tissue to expose the jawbone. They then place and secure the bone graft material in the area needing bone augmentation.
- Healing Process: The healing process can take several months, during which the graft integrates with the existing bone. Your dentist monitors your progress and ensures proper healing.
Post-Procedure Care
After the bone graft procedure, follow your dentist’s instructions for post-operative care:
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain good oral hygiene practices to prevent infection.
- Diet: Stick to a soft diet and avoid chewing on the graft site.
- Follow-Up Visits: Attend all scheduled follow-up visits to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Conclusion
Bone grafts in dentistry are vital for patients needing restorative procedures, particularly dental implants. By understanding their types , their necessity, and what to expect during the procedure, patients can make informed decisions about their dental care. If you are considering a bone graft, consult with your dentist to determine the best course of action for your specific needs.
For more insights and updates on dental solutions, visit udenzo.io. Don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on social media for the latest in dental health news!