Prep and Aftercare Before Sedation Dentistry for Kids
The best way to make sure your child has a pleasant experience at the dentist is to prepare them in advance. Before the Prep and Aftercare Before Sedation Dentistry for Kids for toddlers do the following at home:
- Do not give your child solid food.
- Dress your child comfortably in loose, or loose-fitting clothing.
- Remember to let the dentist know if your child takes any over-the-counter medications or prescriptions.
- Bring a favorite toy! Comfort items, such as stuffed animals
- Preparing your child sedating a child for dental work
Care Instructions After Sedation Dentistry for Kids
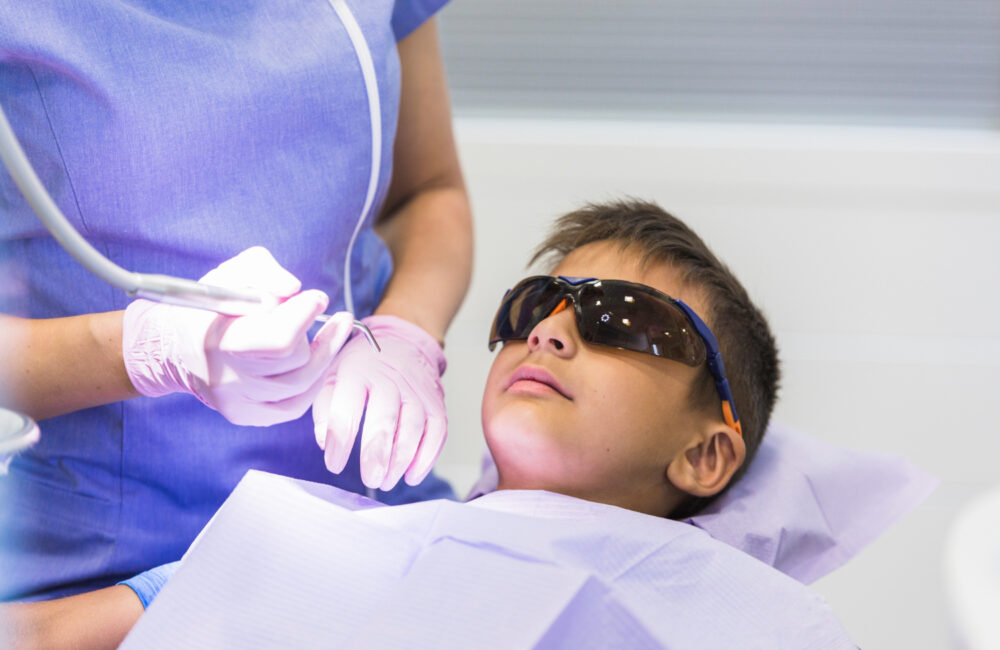
Grogginess, nausea, loss of coordination, and fitful giggles are all common side effects of sedation for toddler dental work. Your child will need a few days to recover. Remember to:
- Observe your child after the procedure.
- Serve them mashed vegetables, lukewarm soups, or smoothies to soothe their mouths.
- Make sure your child is hydrated with water.
- Apply an ice pack if swelling occurs.
Dentists can safely administer sleep sedation. Ask them about the options available. This will help your child feel more relaxed and comfortable before the procedure. Preparing your child for sedation for toddler dental work can ensure the best possible experience; avoid giving them solid foods, pick out an outfit that is comfortable for your child, and make sure your dentist knows about any medical history your child may have! After the treatment, remember to take extra care of your child.
Uses of Sedation
sedation dentistry for kids will vary depending on the procedure required. For minor dental work, such as crowns or fillings, nitrous oxide usually suffices. Nitrous oxide is regarded as the safest sedative, in large part due to its immediate effect and ease of use. For most patients, there is no long-term effect. Minor side effects, such as headaches and nausea, are rare.
An oral sedative can be prescribed for any type of dental procedure, but it is most commonly used in complex procedures such as tooth extraction and oral surgery. Furthermore, it can be used by patients with severe dental anxiety or special needs to undergo routine exams or cleanings.
IV sedation may be used to perform more complicated oral surgeries, such as extraction of wisdom teeth or gum grafting. It is especially useful for patients who have to sit in the dental chair for an extended period.
Invasive procedures, such as jaw surgery, usually require a child under anesthesia for dental work. To learn more contact Luna Pediatric Dentistry in Richmond.
Related / Discover IV Sedation Dentistry!
Sedation Safety
Is dental sedation safe for kids and toddlers Are you wondering if laughing gas safe for children’s dental work? The answer to all three questions is yes. Sedation dentistry for kids is a completely safe procedure for most patients. Your dentist will get a complete medical history before administering it to ensure that sedation is safe for your child. This will help reduce the risks of certain medical conditions and the effects of anesthesia or sedation, such as 2-year-old dental anesthesia, 4-year-old dental sedation, and dental sedation for 3-year-old
According to a 2009 study, children under 6 may have a greater risk of adverse events. Studies show that toddlers under the age of six have a smaller airway that is easily blocked. Experts say that toddlers do not have the same reserve of oxygen as older children, so their bodies cannot compensate for short oxygen gaps.
Also, to help ensure your child’s safety, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Dentistry has updated guidelines when administering general anesthesia and deep sedation to children. Dental professionals must follow the below guidelines.
A minimum of two people must always be present. They must know how to provide advanced life support in an emergency. One person will be an oral surgeon or dentist performing the procedure, and the other will act as an independent observer. The independent observers must be nurses, dentists, dental anesthesiologists, or physicians.