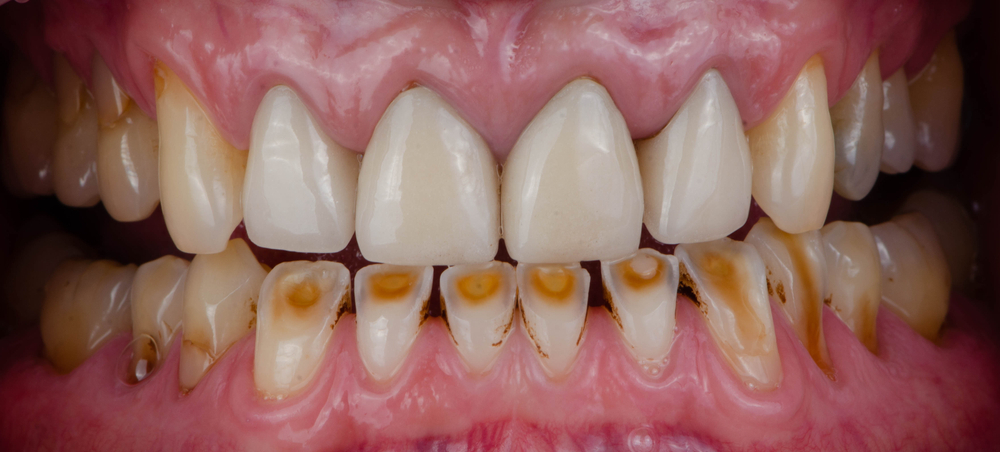
Dental attrition is the loss of tooth structure or tissue caused by tooth-on-tooth contact. Although this type of tooth wear is considered part of the normal aging process, more rapid attrition may be due to larger dental problems. Over time, if the attrition is left untreated, it can wear away the enamel, exposing the dentin of the tooth. This can lead to tooth sensitivity and decay.
Causes of Dental Attrition
The most common cause of dental attrition is bruxism, the grinding and clenching of the teeth that occurs during sleep, usually due to muscle hypertonicity or tension. Bruxism can lead to other health problems, such as sleep apnea and temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ) within your jaw.
Another cause of teeth attrition is bite misalignment. If your teeth are not aligned properly, they could be rubbing together. Over time, the surface of one tooth can start to wear away the tooth surface and enamel of the other. If not treated early on, the damaged tooth enamel can start to accumulate bacterial deposits and lead to cavities, as well as tooth sensitivity and pain.
Signs of Dental Attrition
In addition to tooth sensitivity and decay, other signs and symptoms of attrition include:
- Changes in tooth shape
- Loss of tooth structure
- Tooth pain
- Sore gums
- Tooth discoloration
- Damage to dental fillings and restorations
- In severe cases, tooth loss can occur.
How to Treat Attrition and Prevent Further Damage
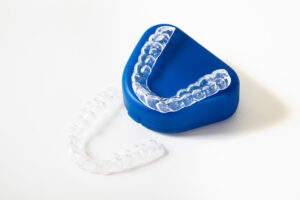
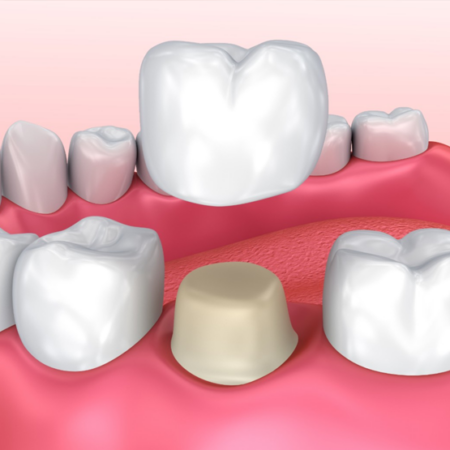
Depending on the cause of tooth attrition, there are various treatment options. Most commonly, dental attrition treatment will involve a combination of orthodontic treatment to fix tooth alignment (e.g. Invisalign), dental restorations to fix damaged teeth, and treatment for Bruxism (e.g. wearing a night guard).









Leave a Reply